Preferential voting
There are many different types of preferential voting systems in use across Australia and the world. This includes both ‘simple majority’ and ‘preferential’ systems.
First-past-the-post
Elections that use a simple majority, or first-past-the-post, system elect a candidate who has received the most number of votes in a contest following a single count. This is regardless of whether or not the number of votes for the successful candidate represents a majority of the total amount of votes.
First-past-the-post voting systems are used in many countries including the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada and India.
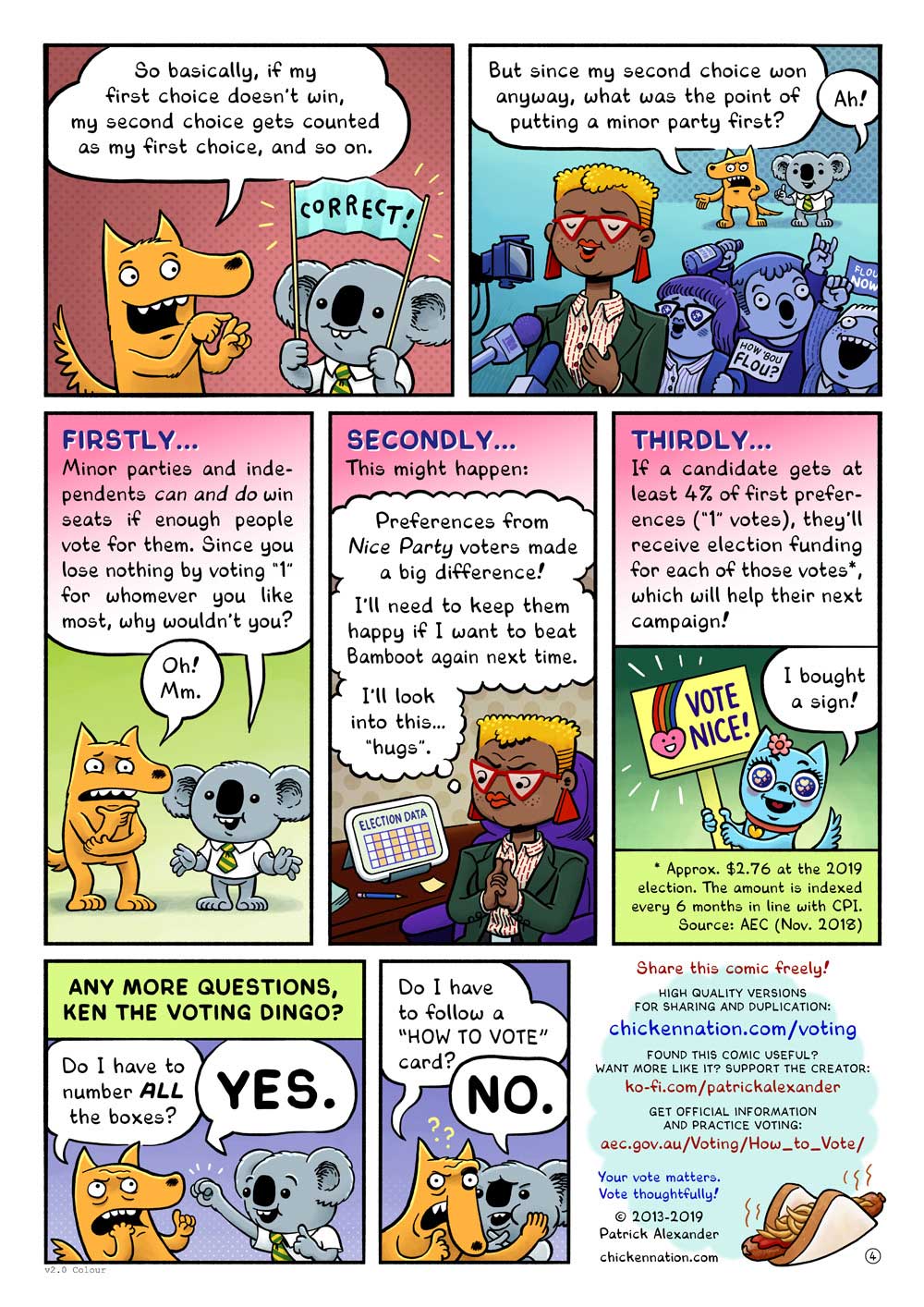
Preferential voting
There are many different types of preferential voting systems in use across Australia and the world.
Some preferential voting systems make it compulsory for voters to mark a preference for every single candidate on the ballot paper, some require a certain number of preferences to be indicated and others are optional preferential.
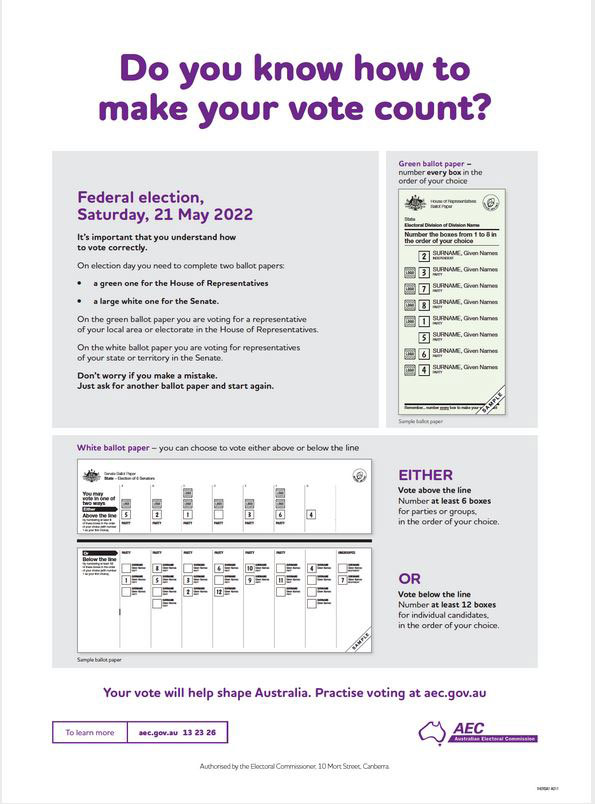
Australian federal elections use a preferential voting system where voters are required to:
- mark a preference for every candidate on the green ballot paper (House of Representatives)
- mark a preference for a designated number of preferences on the white ballot paper (Senate)
Related: How to complete my ballot paper
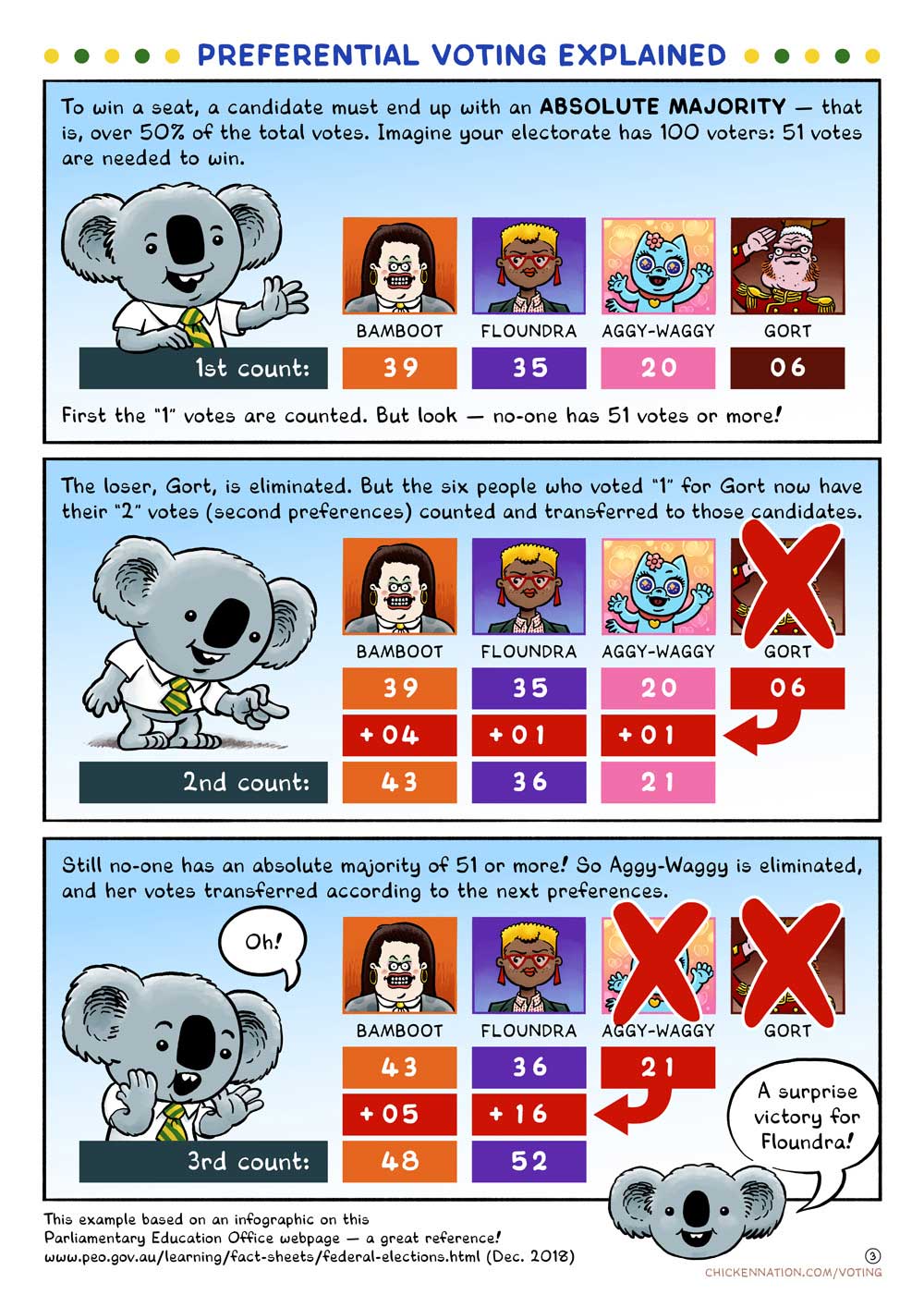
House of Representatives
Each House of Representatives contest will elect a single representative.
The preferential voting system used for the House of Representatives provides for multiple counts of ballot papers to occur to determine who has acquired an absolute majority of the total votes (more than 50% of formal votes).
During the counting process, votes are transferred between candidates according to the preferences marked by voters.
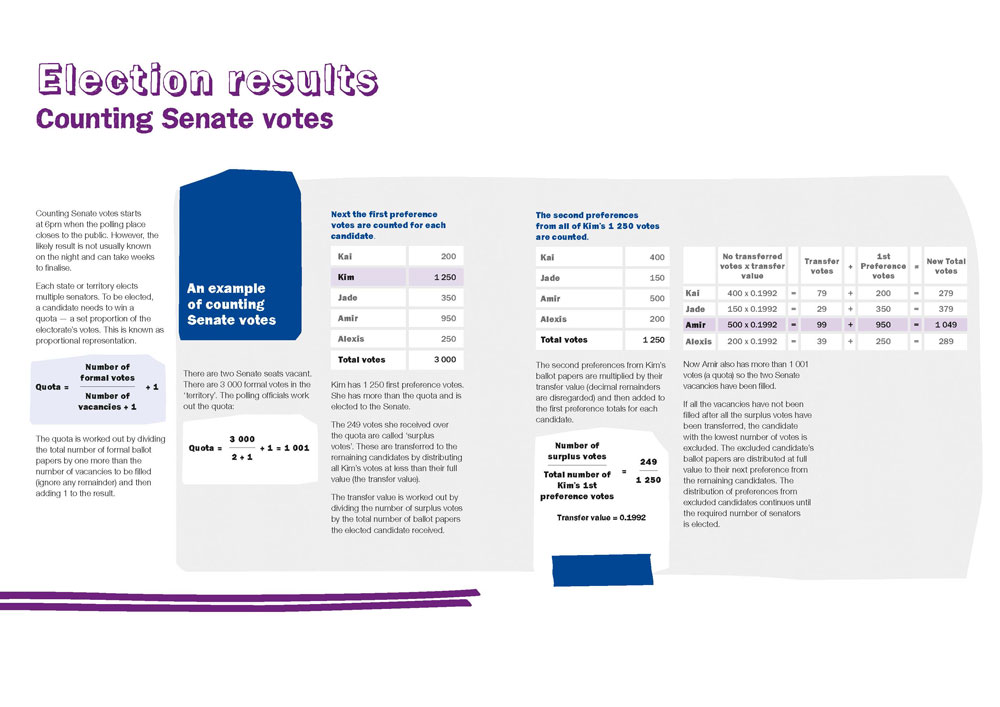
Senate
Each Senate contest will elect multiple representatives.
The preferential voting system used for the Senate provides for multiple counts of ballot papers to occur to determine which candidates have achieved the required quota of formal votes to be elected.
During the counting process, votes are transferred between candidates according to the preferences marked by voters.